Sanction screening is mandatory under MLR 2017. Everyone knows that.
What nobody tells you is how actually to do it. HMRC demands adequate systems, but won’t define adequate. OFSI expects comprehensive screening but publishes no practical standards.
You’re left checking names against spreadsheets, wondering if your process would survive scrutiny, and hoping a similar name doesn’t become your £50,000 mistake.
This guide eliminates the guesswork. Completely free.
In the next 15 minutes, you’ll learn the screening requirements for your practice, the checking process that meets regulatory expectations, how to handle matches and document decisions that protect you, and how to build effective screening without expensive systems.
Key Points Summarised
- Electronic verification is mandatory under MLR 2017. Visual passport inspection doesn’t satisfy legal requirements
- Manual sanction screening costs £500 to £1,500 monthly in lost time. At 15 to 45 minutes per client, you’re spending hours on work that automated systems complete in seconds
- Sanctions compliance differs from AML. The 50% ownership threshold for sanctions control differs from the 25% beneficial ownership test
- OFSI reporting is immediate and separate from SARs. You must report as soon as you know or suspect someone is sanctioned
- Technology eliminates the choice between speed and compliance.
- Penalties start at £5,000 and scale to £1 million or 50% of breach value. Criminal prosecution can result in seven years imprisonment
What is Sanction Screening and Why It’s Crucial for UK Accountants
Sanction screening is the process of checking individuals, entities, and transactions against government-maintained lists of restricted parties. It’s a legal requirement under UK financial sanctions regulations.
The UK Consolidated Sanctions List contains over 57,000 active records across more than 300 programmes maintained by the Office of Financial Sanctions Implementation. The screening process compares client names, dates of birth, addresses, and entity registration numbers using fuzzy matching algorithms to catch name variations and transliterations.
Screening extends beyond your direct client. You must verify:
- Beneficial owners
- Counterparties receiving funds
- Third parties providing payments
Screening must occur at client onboarding before accepting funds, during ongoing monitoring at least annually, at the transaction level when transferring funds to new payees, and whenever circumstances change materially.
Did You Know? Sanctions Come in Four Types
Most firms only think about financial sanctions, but the UK operates four distinct regimes that often overlap:
- Financial sanctions freeze assets and prohibit transactions with designated persons
- Trade sanctions restrict imports, exports, and services to specific sectors or countries
- Sectoral sanctions target particular industries like energy or defence without blacklisting entire jurisdictions
- Travel bans prevent designated individuals from entering the UK territory
A client clear on financial sanctions might still trigger trade or sectoral restrictions depending on their business activities and the services you provide.
The UK Sanctions Landscape in 2026: Key Compliance Updates
The UK sanctions regime exists to prevent money flows to terrorists, weapons proliferators, human rights abusers, and hostile governments. Unlike persuasive foreign policy tools, sanctions carry the force of criminal law.
The UK Sanctions Landscape Post-Brexit
The Sanctions and Anti-Money Laundering Act 2018 established the UK’s independent sanctions framework after leaving the European Union. The Office of Financial Sanctions Implementation administers financial sanctions under HM Treasury.
UK sanctions often align with UN Security Council resolutions but can diverge from EU and US programmes. This creates complexity for firms serving international clients, as you may need to comply with multiple overlapping regimes simultaneously. General licences permit certain activities that would otherwise breach sanctions, while specific licences can be applied for on grounds set out in the relevant legislation.
Every UK business and individual must comply with the sanctions regime, regardless of sector or service type. The sanctions regime operates independently of AML requirements, meaning firms outside the Money Laundering Regulations 2017 still have full obligations.
Recent Enforcement Actions That Should Worry You
OFSI’s 2025 enforcement against GVA Capital demonstrates the scale of penalties now being imposed. The £216 million fine related to Russia and Ukraine sanctions breaches marked a significant escalation in enforcement intensity.
Between 2022 and 2025, OFSI issued over 30 monetary penalties and published details of numerous breaches, even where no fine was imposed. Publication itself damages reputation and signals to clients, banks, and insurers that your compliance framework failed.
Sanction Screening Is Just One Part of Your AML Obligations
Sanction screening sits within broader anti-money laundering requirements under MLR 2017. Customer due diligence, beneficial ownership verification, risk assessments, ongoing monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting all form part of your complete compliance framework.
Understanding Your Legal Obligations for Sanction Screening Under MLR 2017
The Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017 set out your customer due diligence obligations. These requirements work alongside sanctions legislation to create your complete compliance framework.
Electronic Verification vs Visual Inspection
MLR 2017 Regulation 28 requires you to verify customer identity using documents, data, or information obtained from a reliable and independent source. The keyword is “independent.”
Looking at a passport and making a photocopy constitutes visual inspection. It proves you received a document, but it doesn’t prove you verified that document against any authoritative source. Electronic verification means checking the identity information against databases maintained by credit reference agencies, the electoral register, or government systems like the Passport Office or DVLA.
When You Must Screen
You must screen when establishing a business relationship, which occurs at client onboarding, before accepting any funds or commencing substantive work.
Ongoing monitoring requires periodic rescreening based on your risk assessment. High-risk clients may need quarterly checks. Standard-risk clients should be rescreened annually or when circumstances change materially.
Transaction-level screening applies when payments involve third parties or counterparties you haven’t previously verified. Sanctions lists update constantly, so you must check the current lists when conducting any screening activity.
Reporting to OFSI: Timelines & Requirements
You must report to OFSI as soon as practicable when you know or have reasonable cause to suspect that a person is a designated person or has committed an offence under the sanctions regulations. “As soon as practicable” means immediately upon discovery.
Reports must use OFSI’s standard template and include details of the suspected person, the grounds for suspicion, any assets frozen, and relevant transaction history.
If you discover you’re holding funds for a designated person, you must freeze those assets immediately and report them to OFSI. The frozen funds cannot be released without a specific licence.
Penalties: Civil & Criminal Consequences
OFSI can impose civil monetary penalties up to £1 million or 50% of the breach value, whichever is greater. The regime operates on a strict liability basis, meaning unintentional breaches still attract penalties.
Criminal prosecution under the sanctions regulations can result in imprisonment for up to seven years, an unlimited fine, or both.
OFSI’s enforcement guidance confirms that they take a risk-based approach when deciding whether to impose penalties. Factors considered include whether the breach was reported voluntarily, whether appropriate due diligence was conducted, and whether the breach resulted from attempting to circumvent sanctions.
Beyond Sanction Screening: Your MLR 2017 Obligations
You’ve covered sanction screening. Now understand the complete AML framework you’re operating under, from customer due diligence to suspicious activity reporting.
2025 Anti-Money Laundering ID Check Guide for Accountants in the UK – FigsFlow
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Conduct Effective Sanction Screening in the UK
Effective screening combines customer due diligence, electronic verification, comprehensive list checking, and ongoing monitoring within an integrated workflow that creates complete audit trails automatically.
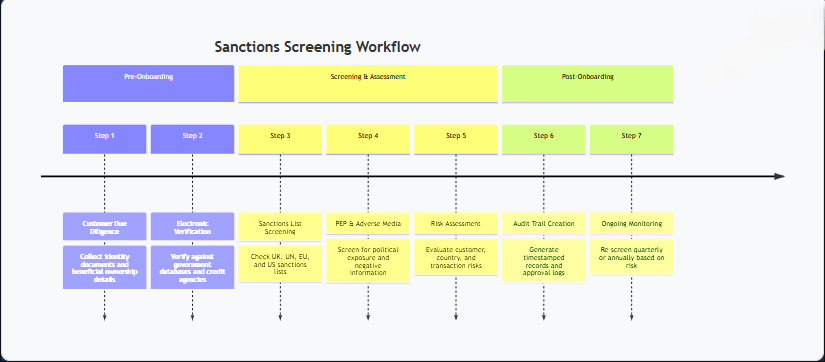
Step 1: Customer Due Diligence
For individual clients, collect full legal name, date of birth, residential address, and nationality. For company clients, obtain the legal entity name, registration number, registered office address, and details of all persons with significant control.
Remember that beneficial ownership under sanctions uses a 50% threshold, not the 25% threshold in MLR 2017. Control can also arise through voting rights or board appointments.
Step 2: Verify Against Government Databases
Use electronic verification to check identity details against credit reference agencies (Equifax, Experian, TransUnion) or government registers (Passport Office, DVLA, electoral register). The process reads the machine-readable zone on passports and driving licences to confirm documents exist in official records.
For companies, use Companies House API to verify incorporation details, current officers, and PSC information in real time.
Wouldn’t It Be 100X Easier if Your Onboarding Software Connected With Companies House?
Well, you’re in luck. The complete client onboarding platform FigsFlow connects not only with Companies House, but with Xero, HubSpot, and more.
Want to give it a try? Here’s your 30-day free trial.
Step 3: Screen Against Sanctions Lists
Check the UK Consolidated Sanctions List maintained by OFSI as your primary screening source. Include UN Security Council designations and EU sanctions lists if you have European operations or clients.
Screen against the US OFAC lists if transactions are denominated in US dollars or touch US financial systems, as OFAC has extraterritorial reach.
Step 4: Check PEP Status & Adverse Media
Identify whether the client is a Politically Exposed Person under MLR 2017. PEP status triggers Enhanced Due Diligence requirements, including establishing the source of wealth, the source of funds, and the business relationship purpose.
Search news sources, enforcement databases, and legal proceedings for negative information about the client.
Step 5: Assess & Document Risk
Evaluate customer risk factors (PEP status, ownership complexity, sector), country risk (sanctions jurisdictions, weak AML frameworks), and transaction risk. Determine whether Standard Due Diligence or Enhanced Due Diligence applies.
Document your assessment with clear reasoning for your risk rating and due diligence level.
Step 6: Create Complete Audit Trails
Generate timestamped records showing who conducted verification, which databases were checked, what results were returned, how you assessed risk, and who approved the client. Keep these records for five years after the relationship ends.
Automated systems create audit trails as a byproduct of normal operations rather than requiring separate documentation.
Step 7: Ongoing Monitoring
Rescreen high-risk clients quarterly and standard-risk clients annually or when circumstances change materially. Subscribe to OFSI email alerts to receive immediate notification of new designations, as sanctions lists update daily.
Looks Like a Lot of Steps for Just One AML Component?
Don’t worry. FigsFlow has got you covered.
It’s a complete client onboarding platform that handles everything from proposals and engagement letters to electronic verification, sanction screening, PEP checks, and automated audit trails. All in under 30 seconds per client.
Here’s what you get beyond sanction screening:
- Professional proposals and engagement letters in minutes
- Electronic ID verification (MLR 2017 compliant)
- Risk assessment templates aligned with HMRC guidance
- Built-in e-signature with automated workflows
- Integrations with HubSpot, Xero, QuickBooks, Stripe
All of this comes at the price of just £18/month (verification at £2.10 per check).
Start Your 30-Day Free Trial – No credit card required.
What to Do When You Identify a Sanctioned Person: Immediate Actions for UK Firms
Discovering a client is sanctioned creates immediate legal obligations. The speed and completeness of your response determine whether OFSI views this as a compliance success or failure.
Immediate Actions: Freeze, Report, Document
Stop all work immediately. If you’re mid-transaction, halt it. If you hold client funds, freeze them. No payments out, no payments in.
Notify your Compliance Officer for Legal Practice (COLP) or equivalent compliance lead immediately. They coordinate the firm’s response and ensure all necessary actions occur.
Contact your bank to notify them you’re holding frozen funds. They may need to take their own compliance actions and will refuse to process transactions involving the sanctioned client without appropriate licences.
How to Communicate with Clients (No Tipping-Off Rules)
Sanctions are public information. Unlike suspicious activity reports under the Proceeds of Crime Act 2002, there’s no tipping-off offence preventing you from explaining to the client why you’re suspending services.
You can tell them clearly and directly that they’ve been designated under UK sanctions, which restricts your ability to provide services or handle their funds.
Explain that you cannot release their funds without an OFSI licence, even if they dispute their designation.
Licensing Options: When You Can Continue Services
General licences permit certain activities without application. Legal services licences exist under some sanctions regimes, allowing you to provide legal advice and representation on an unpaid basis or subject to conditions.
Specific licences require an application to OFSI. You’ll need to demonstrate that the grounds set out in the implementing legislation apply to your situation.
Both general and specific licences come with reporting obligations. You must notify OFSI of your reliance on general licences within specified timeframes.
The Secret to Catching Sanctioned Persons Early
Consistent identification starts with an effective AML policy that embeds sanction screening into your workflows. Here’s how to build yours.
Sector-Specific Red Flags: How to Spot Sanction Evasion in Your Industry
Sanctions evasion attempts follow predictable patterns. Recognising red flags in your practice area allows you to investigate further before proceeding with potentially problematic engagements.
| Risk Category | Red Flags | What to Investigate |
|---|---|---|
| Politically Exposed Persons | Current or former senior government officials, military leaders, judges, central bank executives, state-owned enterprise directors | Source of wealth, source of funds, purpose of the relationship. Enhanced Due Diligence is mandatory regardless of other factors. |
| High-Net-Worth Individuals | Investable assets exceeding £30 million combined with wealth from sanctioned jurisdictions, unexplained funds, or resistance to due diligence | Origin of wealth, connections to sanctioned jurisdictions, reason for due diligence resistance |
| Complex Corporate Structures | Multiple holding companies, offshore entities in secrecy jurisdictions, frequent restructuring without operational changes | Beneficial ownership chain, business rationale for structure, operational substance |
| Trusts | Established in children's names shortly before settlor designation, unclear purpose, frequent term changes | All settlors, trustees, and beneficiaries. Changes redirecting benefits to new persons. |
| Russia-Connected Jurisdictions | Russia, Belarus, Cyprus, Moldova | Direct and indirect connections to Russian designated persons, economic ties to sanctioned entities |
| Sanctioned Countries | Myanmar, Syria, Iran, North Korea, Afghanistan | Any client connections, transaction flows, and beneficial ownership links |
| FATF High-Risk Jurisdictions | Countries on the grey list (increased monitoring) or the black list (countermeasures) | Strategic AML deficiencies, adequacy of the client's own compliance procedures |
| Offshore Financial Centres | British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Jersey, Guernsey, Panama | Whether used for legitimate tax planning or ownership obfuscation, ultimate beneficial owners |
| Real Estate Transactions | Cash purchases, newly established buyer entities, no connection to property location, investment properties never occupied | Source of purchase funds, reason for entity structure, connection to property |
| Trust Administration | Changes to trust terms, new beneficiaries added, indirect benefits to family members | All parties separately verified, reason for the term changes, the ultimate beneficiaries |
| International Trade | Imports/exports to sanctioned jurisdictions, dual-use goods, circuitous shipping routes through high-risk countries | Trade sanctions compliance, end-use of goods, reason for routing |
| Litigation Funding | Disputes involving Russian or Middle Eastern parties | Ultimate funding sources, beneficial parties to dispute outcome |
