Before accepting any new client, UK law requires you to verify that they are not subject to financial sanctions.
Missing this check can cost your firm thousands, if not millions, in fines and penalties. There are even cases where individuals have received up to seven years of imprisonment.
It is not a question of whether you do sanction screening or not. The real question is, how do you do it effectively?
This guide walks you through the practical steps for effective sanctions screening. You’ll learn who needs to screen, when to screen, and exactly how to perform checks that keep your business compliant.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Sanction screening is mandatory for all UK businesses, not just those in financial services, and applies to clients, counterparties, beneficial owners, and third parties involved in transactions
- The UK sanctions regime carries strict liability, with penalties up to £1 million or seven years’ imprisonment for breaches, even if unintentional
- Effective screening requires checking ownership structures beyond 50% shareholding, as control can be exercised through board appointments or influence over company affairs
- Screening must happen at client onboarding and through ongoing monitoring, as the UK sanctions list updates frequently with new designations added regularly
- Red flags include complex ownership structures, resistance to due diligence, involvement of high-risk jurisdictions, and transactions without clear business rationale
- If you identify a designated person, you must immediately freeze assets, stop work, report to OFSI, and apply for a licence before continuing any services
What Is Sanction Screening?
Sanction screening is the process of checking whether individuals, entities, ships, or aircraft appear on official sanctions lists before you do business with them.
What is Sanction Lists?
A sanctions list is a government-maintained register of individuals and organisations subject to legal restrictions. In the UK, the Office of Financial Sanctions Implementation (OFSI) administers the consolidated sanctions list. This list includes people and entities involved in terrorism, human rights abuses, weapons proliferation, and other activities threatening international peace and security.
Sanctions are not just names on a list. They represent legal restrictions that can include asset freezes, travel bans, and prohibitions on providing specific services. When you screen clients, you are verifying they are not subject to these measures.
The UK sanctions regime operates independently from the EU since Brexit. While there is overlap with UN, EU, and US sanctions lists, UK businesses must primarily comply with UK designations. However, if your firm has international exposure or deals with cross-border transactions, you may need to screen against multiple jurisdictions’ lists.
Screening goes beyond checking a client’s name against a database. You need to understand who owns and controls the entities you are dealing with. Sanctions often apply to companies owned or controlled by designated persons, even if the company itself is not directly listed. This means identifying beneficial owners and understanding corporate structures forms a critical part of effective sanction screening.
Who Needs to Perform Sanction Screening (And When)
Every UK business must comply with sanctions regulations. This isn’t limited to banks or financial institutions.
Law firms, accounting practices, real estate agents, import/export companies, charities, and even tech startups all fall under the sanctions regime. If you handle client money, facilitate transactions, or provide professional services, you need to screen.
The obligation extends across all business sectors. OFSI has published specific guidance for charities and non-governmental organisations, signalling that enforcement isn’t just focused on financial services anymore.
When to Perform Sanction Screening?
It depends on the natural of your business activity. Typically, you must screen sanction list at the start of new client relationship, before accepting funds, and whenever your client’s circumstances change materially.
Sanction list changes constantly. So, ongoing monitoring is essential, and firms should rescreen clients at list annually, or when significant list changes occur. With the 28 January 2026 transition approaching, businesses should prioritize sanction screening before this date to ensure compliance with the latest regulations.
Time-sensitive situations require immediate screening. If you’re about to release funds, complete a property transaction, or finalise any deal, current sanctions status must be verified.
Some firms only discover sanctions issues when a counterparty in a transaction turns out to be designated. This is why screening can’t focus solely on your direct client but must extend to beneficial owners, third parties providing funds, and transaction counterparties.
How to Conduct Effective Sanction Screening
Effective sanctions screening follows a systematic process. Each step builds on the previous one to create a comprehensive compliance framework.
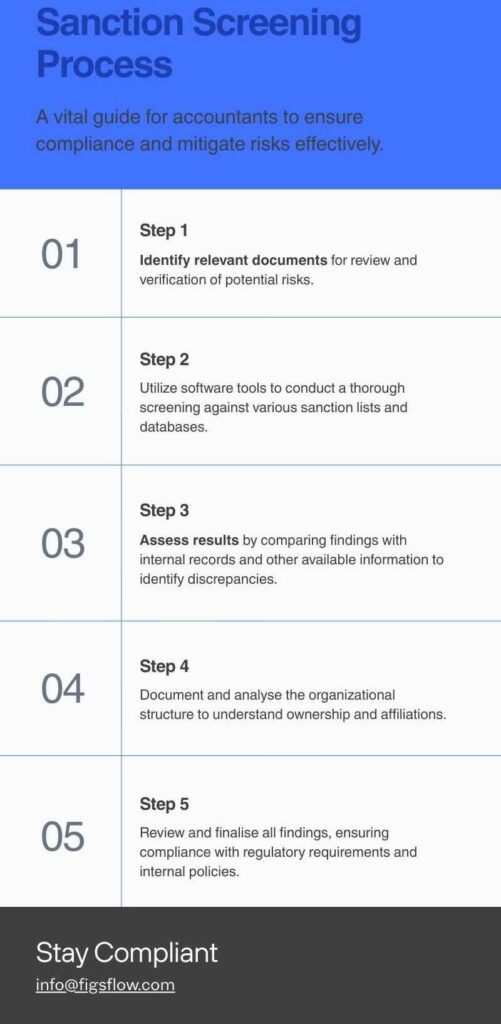
Step 1: Gather Client Information
Start by collecting complete identification details for everyone involved in the matter. For individuals, you need full names, dates of birth, nationalities, and addresses.
For companies and other legal entities, gather the registered business name, registration number, business address, and jurisdiction of incorporation. Don’t stop at the surface level.
You also need information about who owns and controls the entity. This means identifying all individuals with more than 50% shareholding or those who can appoint or remove a majority of the board. It also includes anyone who can ensure the entity’s affairs are conducted according to their wishes.
The 50% ownership threshold for sanctions differs from the 25% threshold in anti-money laundering regulations. This distinction matters when determining who you need to screen.
Collect details about counterparties and third parties too. Anyone providing funds for the transaction, receiving funds, or materially involved in the deal needs to be identified and screened.
Don’t accept client funds before completing this information gathering. Once money enters your client account, you face significant complications if you later discover sanctions issues.
Step 2: Check Against the UK Sanctions List
With client information gathered, check names against the UK consolidated sanctions list. You have two main options for conducting these searches.
The UK government provides a free online search tool at search-uk-sanctions-list.service.gov.uk. This platform searches across all UK sanctions regimes and includes fuzzy matching to catch alternative spellings and name variations.
Enter the individual’s or entity’s name in the search field. The tool searches all parts of sanctions designations, including statements of reasons. You can refine searches by regime, date designated, or type of sanctions imposed.
Commercial screening software offers automation for firms handling high volumes. These platforms integrate with your client management systems and automatically screen against multiple sanctions lists simultaneously, including UK, UN, EU, and OFAC lists.
Technology solutions typically update their databases daily as sanctions lists change. Some updates in real-time as new designations are published.
The screening process must cover everyone you’ve identified in Step 1. This includes the client, all beneficial owners, anyone with control, counterparties, and third parties.
Step 3: Assess Potential Matches
Search results will likely produce matches that need investigation. Not every match indicates genuine sanctions hit.
False positives are common. Someone named John Smith in Manchester probably isn’t the same John Smith designated under a Middle Eastern sanctions regime, but you need to verify this.
Use additional identifiers to distinguish between matches.
- Date of birth is particularly valuable for differentiating individuals with common names
- Nationality, known addresses, and associated entities help narrow down whether a match is genuine
For entities, registration numbers and business addresses help confirm identity. Check whether the registered jurisdiction aligns with the sanctions designation.
Document why you’ve concluded a match is or isn’t your client. This creates an audit trail showing you’ve applied due diligence. Simply dismissing matches without investigation exposes you to regulatory criticism if later challenged.
Step 4: Investigate Ownership Structures
Designated persons often hide behind complex legal structures. Your screening can’t stop at checking the immediate client’s name.
Look through corporate structures to identify ultimate beneficial owners. This means following ownership chains through multiple layers of companies, potentially across different jurisdictions.
Control isn’t always about shareholding. Someone might control an entity through board appointments, contractual arrangements, or informal influence. The UK sanctions regime defines control broadly to include situations where it’s reasonable to expect someone can ensure the entity’s affairs are conducted according to their wishes.
State-owned entities in jurisdictions where senior politicians are designated need particular scrutiny. If a sanctioned premier or minister could influence a state-owned company’s decisions, that company may effectively be under sanctions too.
Trusts add another layer of complexity. You need to identify and screen settlors, trustees, and beneficiaries. Any of these parties being designated could trigger sanctions obligations.
Shell companies registered in offshore jurisdictions often serve to obscure ownership. When you encounter these structures, dig deeper to understand who genuinely controls and benefits from the entity.
Third parties providing funds deserve equal attention. Even if your client isn’t designated, receiving money from or paying money to a designated person creates sanctions issues.
Step 5: Document Your Findings
Create comprehensive records of your entire screening process. This documentation serves multiple purposes.
First, it demonstrates to regulators that you’ve undertaken appropriate due diligence. OFSI considers whether adequate due diligence was conducted when determining penalties for breaches.
Record what searches you performed, which databases you checked, when you conducted the searches, and what results you found. Include details of how you assessed potential matches and why you concluded they were or weren’t genuine hits.
Document your risk assessment for each client and matter. Note any red flags identified and how you addressed them. This shows you’ve applied professional judgment, not just followed a checkbox exercise.
Keep records of all information sources used to verify client identity and ownership structures. If you relied on corporate registry searches, bank references, or other documents, retain copies with your file.
For matches you’ve dismissed as false positives, clearly record your reasoning. Include the specific additional information that allowed you to distinguish your client from the designated person.
These records must be readily accessible. You might need to demonstrate your compliance to regulators, and the quick retrieval of documentation becomes essential.
Step 6: Set Up Ongoing Monitoring
Sanctions screening isn’t a one-time compliance exercise. The UK sanctions list changes regularly as new persons are designated, existing designations are updated, and some sanctions are lifted.
Establish a system for monitoring these changes. OFSI sends email alerts when the sanctions list updates. Subscribe to these alerts to stay informed in real-time.
Set a schedule for rescreening existing clients. Many firms rescreen annually at a minimum, but higher-risk clients may warrant more frequent checks. Some firms rescreen quarterly or even monthly for particularly sensitive relationships.
Rescreen immediately when major geopolitical events occur. When Russia invaded Ukraine, hundreds of new designations were added rapidly. Firms needed to check all existing Russian connections urgently.
Monitor not just your clients but also ongoing matters. A counterparty in a pending transaction might become designated before completion, creating complications.
Automated screening tools can facilitate ongoing monitoring by continuously checking your client database against updated sanctions lists. These systems flag potential issues automatically rather than requiring manual periodic rescreens.
When you identify a client who has become designated after onboarding, act immediately. Freeze any funds held, cease providing services (unless covered by a general licence), and report to OFSI.
Red Flags That Should Trigger Enhanced Screening
Certain characteristics indicate heightened sanctions risk. When these red flags appear, standard screening is not enough. You need to dig deeper, ask more questions, and apply enhanced due diligence before proceeding.
- Complex Ownership Structures – Multiple layers of entities across different jurisdictions deserve extra scrutiny. These arrangements can hide designated persons behind seemingly legitimate corporate facades.
- Resistance to Providing Information – Clients who resist disclosing beneficial ownership or control should raise concerns. Legitimate businesses typically understand compliance requirements and cooperate with reasonable due diligence requests.
- High-Risk Jurisdictions – Transactions involving countries with UK sanctions regimes, like Russia, Belarus, Myanmar, or North Korea, warrant enhanced checks. This includes jurisdictions with significant numbers of designated persons, even without a country-specific regime.
- Newly Established Companies – Companies with limited operating history present challenges. There is less information available to verify ownership and business purpose, and shell companies are often newly created.
- Unclear Business Rationale – Transactions without clear business logic need investigation. If you cannot understand why a particular jurisdiction is involved, why certain intermediaries are necessary, or why the transaction is structured as it is, dig deeper.
- Luxury Goods Transactions – Large transactions involving yachts, private aircraft, high-end property, or expensive art carry elevated risk. These assets are common targets for sanctions evasion.
- Unusual Educational Payments – Large payments for educational expenses at exclusive schools or universities can indicate wealth that might attract sanctions interest, particularly if combined with other risk factors.
- Aggressive Timelines – Pressure to bypass normal checks should raise alarms. Legitimate clients understand compliance requirements and allow appropriate time for due diligence.
- Frequent Structural Changes – Frequent changes in entity names, restructuring without a clear business purpose, or changes in ownership structures can signal attempts to evade detection.
- Unknown Counterparties – Third parties who are previously unknown to your client or whose involvement does not fit the transaction type warrant additional investigation.
When you spot these red flags, do not rush through your screening process. Take the time to gather additional information, consult with compliance specialists if needed, and document your enhanced due diligence thoroughly. Missing a sanctions risk because you did not investigate warning signs leaves your firm exposed to significant penalties.
Choosing and Using Screening Technology Effectively
You have two options for sanctions screening:
- manual checks, or
- technology solutions
Each comes with trade-offs you need to understand.
Manual screening using the free OFSI search tool costs nothing upfront. You visit the government website, enter client details, review matches, and document your findings. For occasional checks, this works fine.
The problem is time. Each client requires multiple searches covering individuals, entities, beneficial owners, and counterparties. You need to check alternative name spellings, investigate ownership structures, and document everything properly. What starts as a quick check becomes hours of work per client.
Then there is the regulatory risk. Manual processes depend on human memory and consistency. Miss a step when you are busy, and you have a compliance gap. Forget to rescreen an existing client, and you could be providing services to someone who became designated months ago. The penalties for these mistakes run into hundreds of thousands of pounds.
Technology solutions solve the time problem, but create a different headache. You need one tool for sanctions screening, another for anti-money laundering checks, a separate system for engagement letters and proposals, other software for pricing, and yet another platform for invoicing.
Managing multiple subscriptions gets expensive. Training staff across different interfaces slows onboarding. Data entry becomes repetitive as you input the same client information into each system. Integration between platforms rarely works smoothly.
Introducing FigsFlow: Your All-in-One Technology Solution
FigsFlow is a comprehensive practice management platform that handles everything related to client onboarding from initial contact to full compliance checks. It offers:
- Proposal and engagement letters generated in less than 30 seconds
- Regulatory-compliant engagement letter templates
- Industry standard service pricing built in
- Compliant e-signature functionality
- AML checks (KYC, CDD, EDD)
- Sanction screening with real-time updates
- Complete audit trail for regulatory requirements
- Integration with QuickBooks and Xero
And this is actually free for the next month. Claim your spot and streamline your entire client onboarding process.
Additional Resources
- Complete Guide to UK Sanction Screening (2025/26): Sanction Screening UK Guide 2025/26 | FigsFlow
- 2025/26 Guide to AML Compliance & Financial Crime: Complete Guide to AML Compliance & Financial Crime Prevention | FigsFlow
- PEP Screening for Accountants & Bookkeepers: Why PEP Screening Matters for Accountants & Bookkeepers | FigsFlow
- Checklists for ID Verification: AML ID Verification Checklist: Essential Steps | FigsFlow
- AML Check Explained: AML ID Verification Checklist: Essential Steps | FigsFlow
Conclusion
Sanction screening is not just a compliance checkbox. It protects your firm from criminal prosecution, million-pound fines, and reputational damage while contributing to international security efforts.
The process requires systematic attention. Gather complete information, screen thoroughly against current lists, investigate ownership structures, document everything, and monitor continuously. Technology helps manage the workload, but human judgment remains essential for assessing genuine risks.
Start building your sanctions compliance framework today. Set up email alerts from OFSI, establish clear procedures for client onboarding checks, and train your staff on their obligations.
With systematic processes and the right tools like FigsFlow, sanctions screening becomes a manageable part of your compliance framework rather than an overwhelming burden.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Sanction screening is the process of checking individuals, entities, ships, or aircraft against official sanctions lists before doing business with them. These checks verify that your clients are not subject to UK government restrictions such as asset freezes, travel bans, or prohibitions on receiving services.
UK citizens and companies worldwide must comply with UK sanctions regardless of where they operate. This includes foreign entities trading within UK borders and subsidiaries of UK companies, even if incorporated abroad. If you are a UK-based accountant, solicitor, or business handling client funds, you must screen clients against the UK sanctions list.
Sanction checks must take place before onboarding new clients and accepting any funds. You should also rescreen existing clients regularly, typically at least annually or more frequently for higher-risk relationships. Immediate rescreening is necessary when major geopolitical events occur or when the OFSI sanctions list updates significantly.
Failing to screen clients can result in fines up to £1 million or criminal prosecution with up to seven years imprisonment. UK sanctions operate under strict liability rules, meaning you can be penalised even if the breach was unintentional or you were unaware of your obligations.
The UK government provides a free online search tool at search-uk-sanctions-list.service.gov.uk. This platform searches across all UK sanctions regimes maintained by the Office of Financial Sanctions Implementation (OFSI). Alternatively, you can use commercial screening software that integrates with your practice management systems.
Yes. Sanctions often apply to companies owned or controlled by designated persons, even if the company itself is not directly listed. You must identify and screen all individuals with more than 50% ownership or those who can control the entity’s affairs. This includes checking counterparties and third parties involved in transactions.

